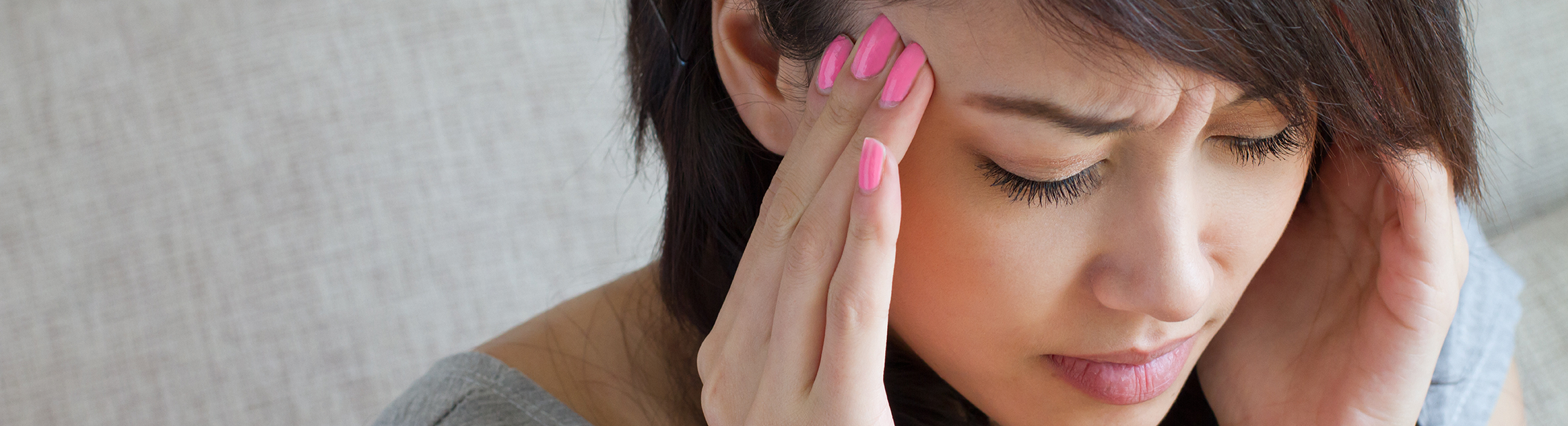
What are Migraine headaches?
Throbbing headaches associated with nausea and vomiting, lightheadedness, sensitivity to light (photophobia), and other visual disturbances are common migraine symptoms.
Migraines are unique in that they have distinct phases. However, not all patients have each phase.
The phases of a migraine headache may include:
+ Premonition phase. A change in mood or behavior that may occur hours or days before the headache.
+ Aura phase. A group of visual, sensory, or motor symptoms that come right before the headache. Examples include visual disturbance, zigzag lines, tunnel vision, distorted vision, vision loss in one field of vision, hallucinations, numbness, changes in speech, and muscle weakness.
+ Headache phase. The period when you experience the actual headache. Throbbing pain occurs on one or both sides of the head. You may also have sensitivity to light and motion.
+ Headache resolution phase. Pain lessens during this phase, but may be replaced with fatigue, difficulty in concentrating, and irritability.
What are the most common types of migraines?
+ Migraine without aura. Patients experience a headache, but no aura.
+ Migraine with aura. These headaches are preceded by aura symptoms, such as a flashing light or zigzag lines. These symptoms usually appear within 30 minutes before an attack. Fewer migraine sufferers have this type of migraine.
Are there specific risk factors?
People with a specific DNA variant on a particular chromosome are at more risk of developing migraines.